A slender woman in a business suit stood at my office door. I guessed her age to be in her early fifties, fifteen or so years older than me. She was attractive and well-dressed. I wondered what she was selling. I stood and invited her in.
“I’m Jeff. What can I do for you?”
As I offered my hand, I realized she was shaking. Her rather limp hand clasped mind and, looking down, she asked quietly, “Can we talk?”
I gestured for her to take a seat as I stepped back behind my desk, sat down, smiled and nodded. I didn’t know it at the time, but we were both destined to be shocked by what would be revealed.
“I’m Elvira’s daughter,” she said.
“Yes, Elvira, she’s a special woman,” I said with a smile.
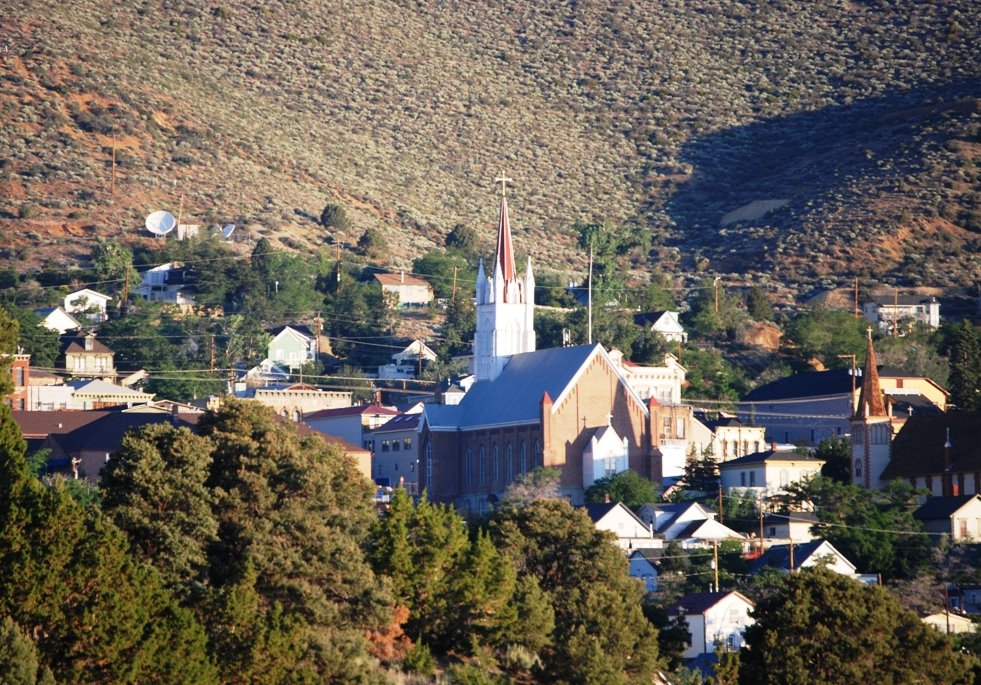
In a few months, I had become very acquainted with Elvira. An elderly woman, she shown up at worship one Sunday morning in late 1993 or early 1994. I don’t remember if it was the first Sunday, but she soon starting requesting each week that we pray for her son, Carl. I included him in our prayers during worship and he remained on the congregation’s prayer list. Over time I learned he lived in Elko, Nevada and was experiencing a relapse of cancer. Elvira was from Nebraska. She now lived in an adult foster home in Cedar City, Utah where I had visited her. The couple who ran the home were happy to see to it that Elvira got to church every Sunday morning and someone from our congregation would give her a ride home. While I was unsure about her living arrangements and her story, she had in a few months become a part of the church’s family.
Sitting in my office, Elvira’s daughter began telling me the story of moving her mother from Nebraska to Utah. At first, Elvira had lived with her daughter and son-in-law at their home in St. George, a town fifty miles south of Cedar City.
“It was a mistake,” she confessed.
At their age, without children of their own, Elvira was like a child. And she had become a wedge between her and her husband. I sensed Elvira’s daughter experienced guilt for having placed her mother in the home but didn’t know what else she could do.
“Are there other siblings who could help?” I asked.
“No,” she said trembling.
“I know you have a brother who has cancer. Is he Elvira’s only other child?”
“Yes. But my brother has been a problem all along. He was married and had a son, but then left his wife for a man. That’s a sin, but my mother just accepts it.”
“Well, he’s her son,” I said.
“Don’t you think that’s a sin?” she asked.
“I didn’t say that,” I responded. “But that’s not the issue. We’re all sinners and to her, he’s also her child, her flesh and blood.”
“He’s always asking my mother for money, and never pays it back.” I could sense she had nothing but disgust for her brother. There was a pause and I waited for her to continue.
“My mother doesn’t have that much, but she he gave him enough for a down payment for that house he and his opera singing lover built in Virginia City.”
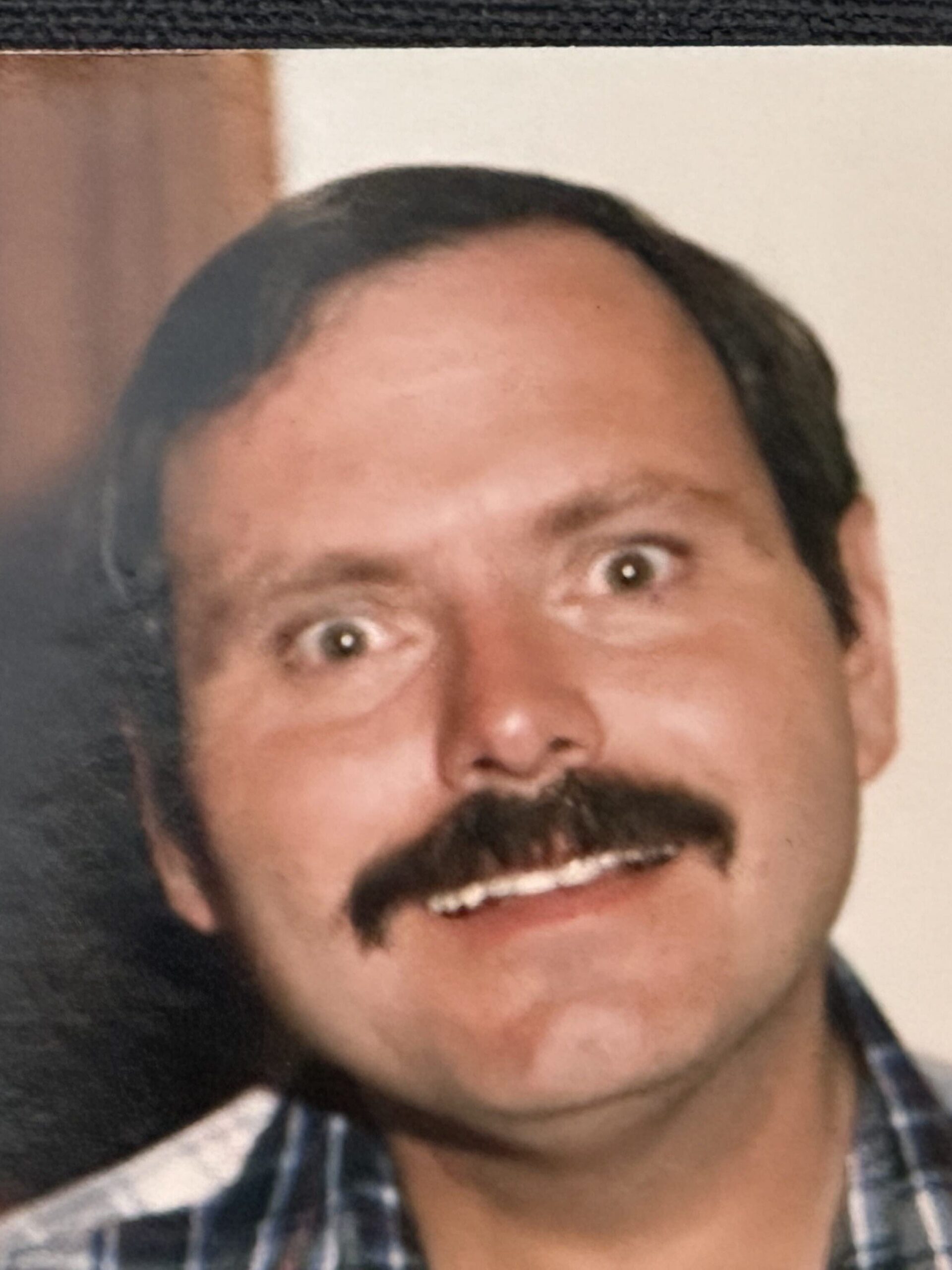

My brain exploded. “It couldn’t be,” I thought. Maybe she sensed my reaction for she stopped and, for a moment, we sat quietly.
“Did your brother also go by the name, Doug?” I finally asked.
She turned white. Her eyes widened. After a moment, she nodded and bowed her head. Finally, she continued. “His name is Carl Douglas. We always called him Carl, but his friends know him as Doug.”
“I know him,” I said, confessing what was now obvious. “I haven’t seen him in three or four years and didn’t know he’d moved to Elko.”
—
Memories of Doug flooded my mind. It seemed so ironic I’d been praying for a couple of months for someone I once knew well.
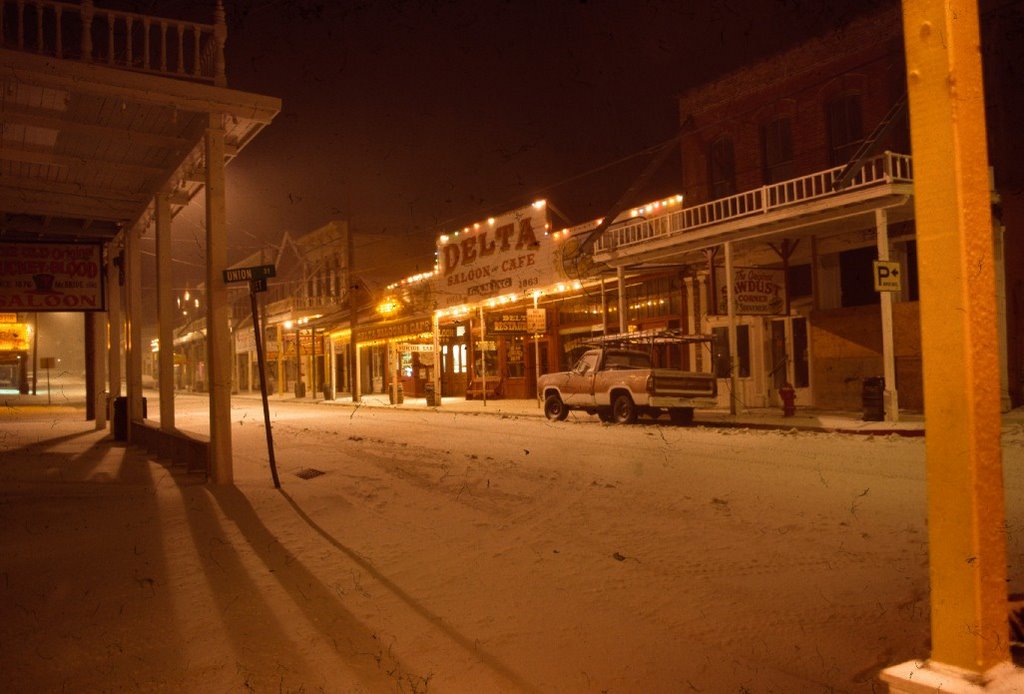
I’d met Doug and Rudi in 1988, right after moving to Virginia City. I was thirty-one years old and a student pastor at a small congregation there for a year. The first week, Doug and Rudi invited me to dinner at their home in the Highlands. Although they were already living there, the house was still under construction. Doug had done most of the work. Before dinner, they showed me around their home in which the kitchen cabinets still lacked doors and there was much trim to be finished. I had the sense they might be gay, which was confirmed when they showed me their master bedroom. I was nervous, looking in, as I’d never been in a bedroom of someone gay. But I almost laughed. I was amazed at how messy it was, which went against my stereotypical images that I had of how gay men lived.
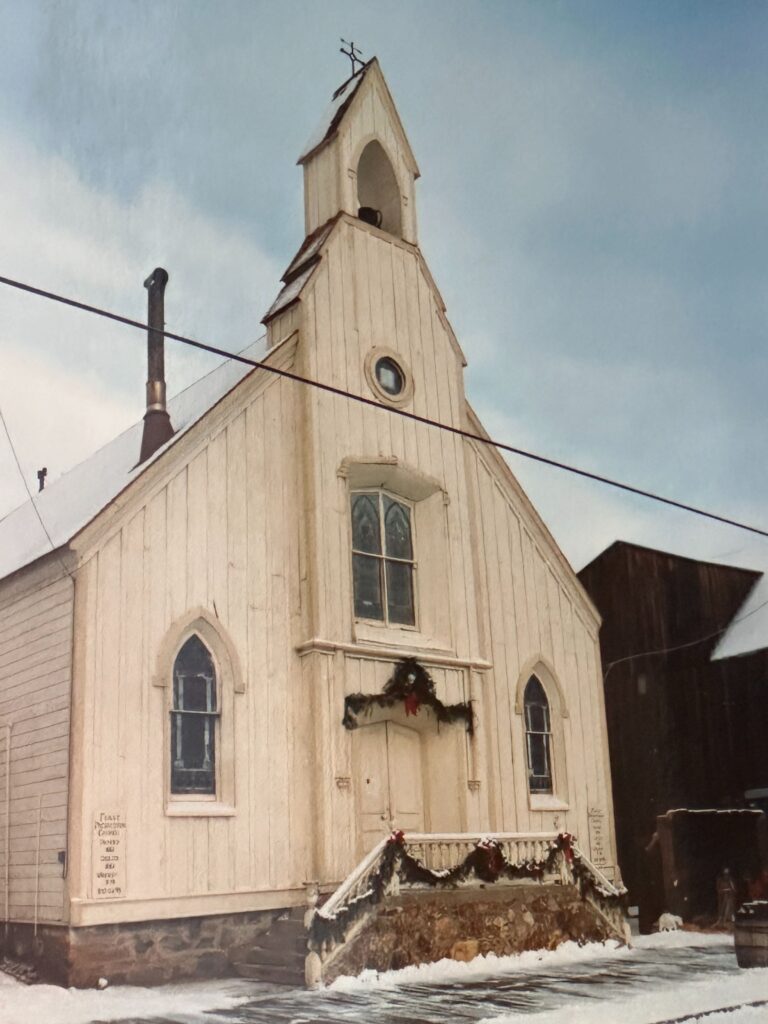

Over the next few months, I got to know them better. Rudi sang at church functions and Doug was our go-to handy man. He built a manger for a nativity display we posted beside the church at Christmas. He had helped me winterize the house I was living in. Later, he’d help design a retaining wall that kept the hill behind the church from encroaching on the sanctuary. By then, though, he was too sick to do the work.
Perhaps my best memory of Doug was from New Year’s Eve, which was a Saturday in 1988. As I practiced my sermon for Sunday that afternoon in the sanctuary, I heard water run under the organ. Upon investigating, I found a crack in the pipe supplying our hot water heating system. I called Doug and he came down immediately with his tools. Together, we spent an hour on our bellies, under the organ, cutting out the damaged pipe with a hacksaw and then soldering in a new piece. We took turns holding the pipe and torch, as we each talked about our plans for the evening. Thanks to our efforts, heat was restored, even though we were both late for our respective parties.
Doug also helped me with my first computer. He ordered the parts and built the computer, showing me how it fit together. This was in January 1989. The computer had 640 kilobytes of RAM, a 30 meg hard drive, and a 5 1/4 floppy disk. He only charged me for the parts. It was still expensive, but about half of what a computer cost in those days (which is more than they cost today). With the coming of a computer, I would never write another sermon by hand.
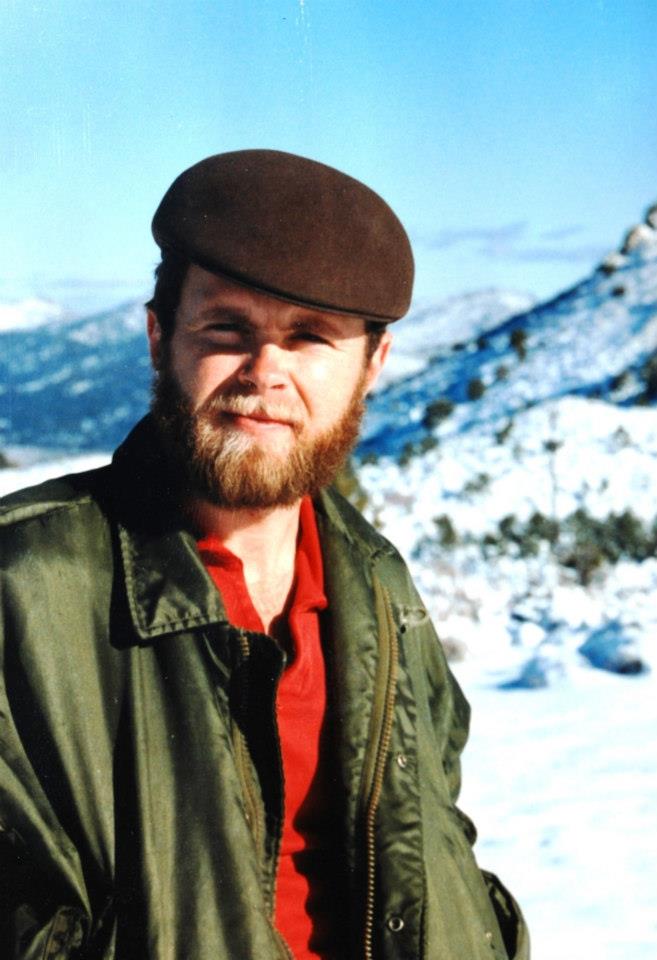

A few months into the new year, Doug became sick. He had tests and asked me to go with him to the doctor to hear the report. It was cancer, lymphoma. The prognosis wasn’t good. The doctor had tears in his eyes as he talked about the prognosis.
Doug soon started chemotherapy. On at least one occasion, I drove him to Reno for his treatments. We’d had a pleasant talk heading down the mountain on Geiger Grade. On the way back, Doug was sick and spend much of the trip with his head in a bag. By late summer, when I was leaving to return to seminary, Doug had lost most of his hair, but he was doing better. In the summer of 1992, when I visited Virginia City, I stayed with him and Rudi. Doug had been in remission for over a year.
Later that year, I’d heard through mutual friends that they had split up. I lost contact with them.

—
I’m sure the room was spinning for Doug’s sister as I told her about my time as a student pastor in Virginia City and how Doug had been very involved in that church. We talked for some time that afternoon, as I tried to encourage her to reconcile with her brother.
I am sure many people would consider this meeting as a coincidence, but I saw God’s hand-written all over it. I had to reconnect with Doug. The phone number Elvira, his mother, had for Doug in Elko no longer worked. I made some calls to friends in Virginia City. No one had heard from Doug in a while, but I was given a phone number for Rudi, who was now living in Las Vegas. Calling him, I was shocked to learn he and his new lover had moved Doug down for Elko. Doug was living with them. He had become so weak that he could no longer care of himself and there was fear he would be homeless.
A few weeks later, as I was coming back from a trip to California, I stopped in Vegas and visited Doug. He was resting on the couch and remained prone the entire time. I was afraid it would be the last time we’d see each other. I could tell that he was pleased I had stopped and that his mother was in the church I served. I stayed only for an hour as Doug appeared exhausted.
It turned out that wasn’t the last time that I saw Doug. A few weeks later, in early September, Rudi called and said that Doug had rallied and wanted to come up and to see his mother and me. The day of the reunion of Doug and his mother was hot with not a cloud in the sky. We toured Cedar City and ate lunch at a Chinese restaurant. By the time lunch was over, Doug was tired. Rudi suggested they head back to Vegas. But before they left, as we stood talking in the parking lot, Doug pulled me aside and asked if I would be willing to officiate at his funeral. He knew it wouldn’t be long. I assured him it would be an honor.
It was just a week or two later when I received the call that Doug had died. He was 48 years old. I went over to Elvira’s to give her the news. She expected it. She wanted to attend the funeral and hoped her daughter would take her. However, her daughter refused, so I offered to drive Elvira down to Vegas.
The day we left, her daughter asked us to stop along the way for dinner. She lived only a mile or so off Interstate 15, so it really wasn’t out of the way. I agreed, secretly hoping I could encourage her to attend the funeral, but she remained adamant. After dinner of hash made from a left-over brisket, that was quite good, we left her home in St. George and continued to Vegas.
As the interstate came out of the Virgin River Gorge, a violent thunderstorm moved through with high winds and blinding lightning that cooled the air from the day’s heat. I slowed down in the driving rain, but it felt as if the storm was cleansing the earth. Elvira and I both marveled at the lightning. That night, we stayed overnight at Rudy’s. Elvira slept in Doug’s old bedroom while I camped out on the couch where Doug had laid when I visited him earlier in the summer.
The next morning, September 30th, I escorted Elvira inside the chapel at the cemetery for one last look at her son. Then they closed the casket. Slowly others gathered. By the time all were present, about a dozen of us, we filled only two rows in the oversized room. Rudi, Doug’s former lover, was there with his new lover. His son had made it. Hilda, who had also been a student pastor in Virginia City a few years before me and was organizing a new church in Green Valley, a Vegas suburb, was there, as was her husband whom she met in Virginia City. A few women who had been friends with Doug and Rudi rounded out the group. On schedule, the chapel’s organist played music. Hilda and I read scriptures and offered prayers. Then Hilda sang a solo and I preached the homily.
Afterwards, we made our way out of the cool chapel into the late-summer heat of a Las Vegas morning, stopping at the gravesite. A few words were spoken, and the party broke up. Elvira and I stopped for lunch and then drove back to Cedar City that afternoon.
Before the end of the year, Elvira moved back to Nebraska, into an assisted living facility. We kept up with each other for a couple of years through Christmas cards, but then her cards stopped coming. I sure she is no longer with us. However, I am glad to have had the privilege to minister to her and to her son. I just wished her daughter could have found a way to reconnect to her brother before it was too late. But I learned that I can’t change people and it’s not my job. Instead, I had to care for all three in what limited ways I could.
About the photos:
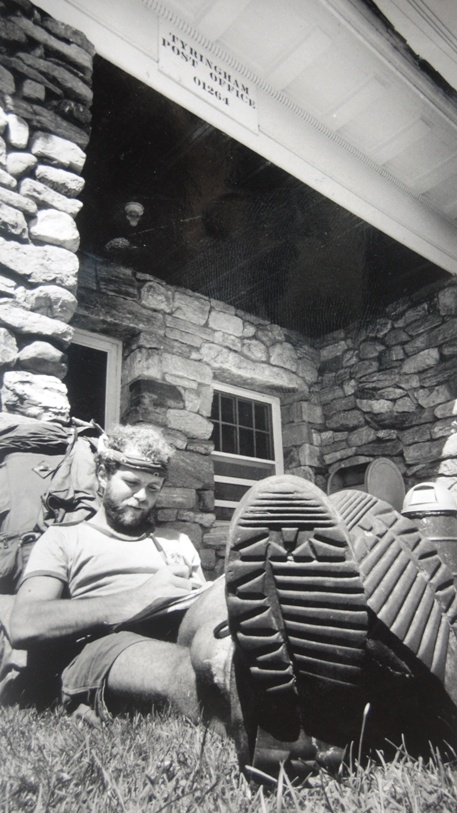
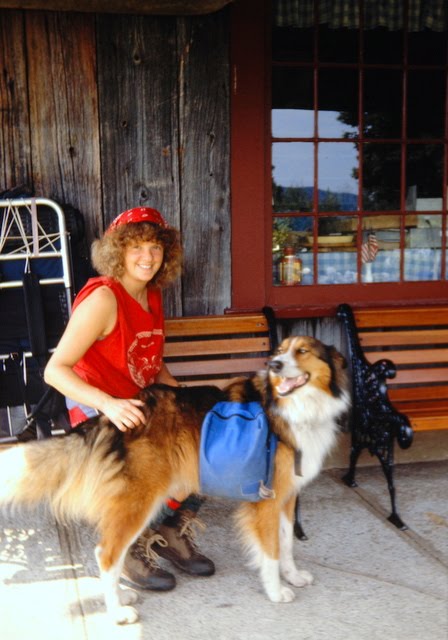
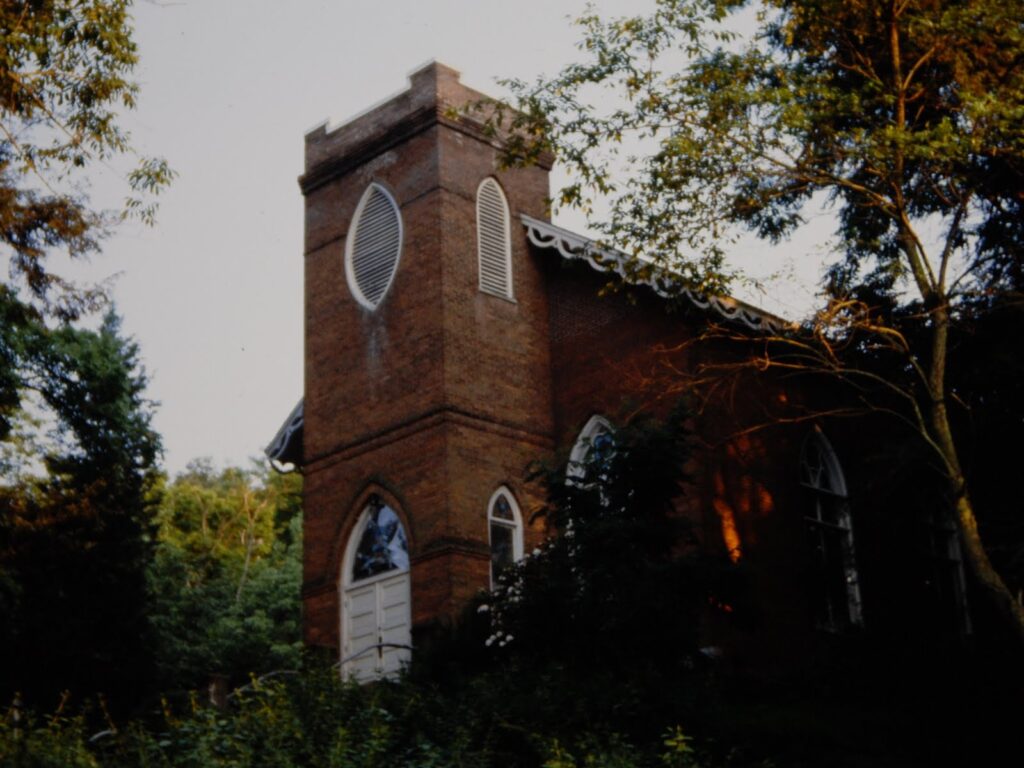
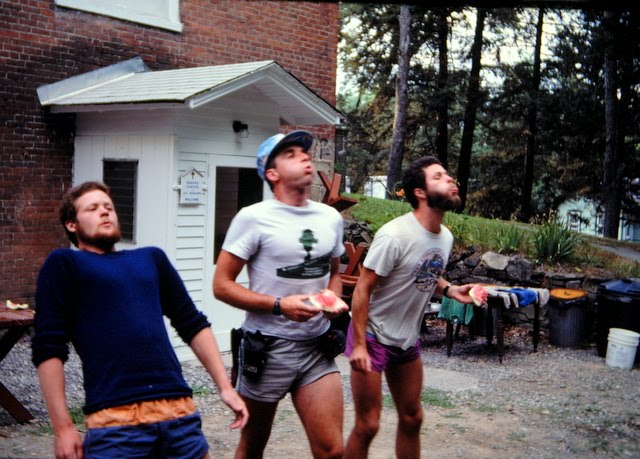
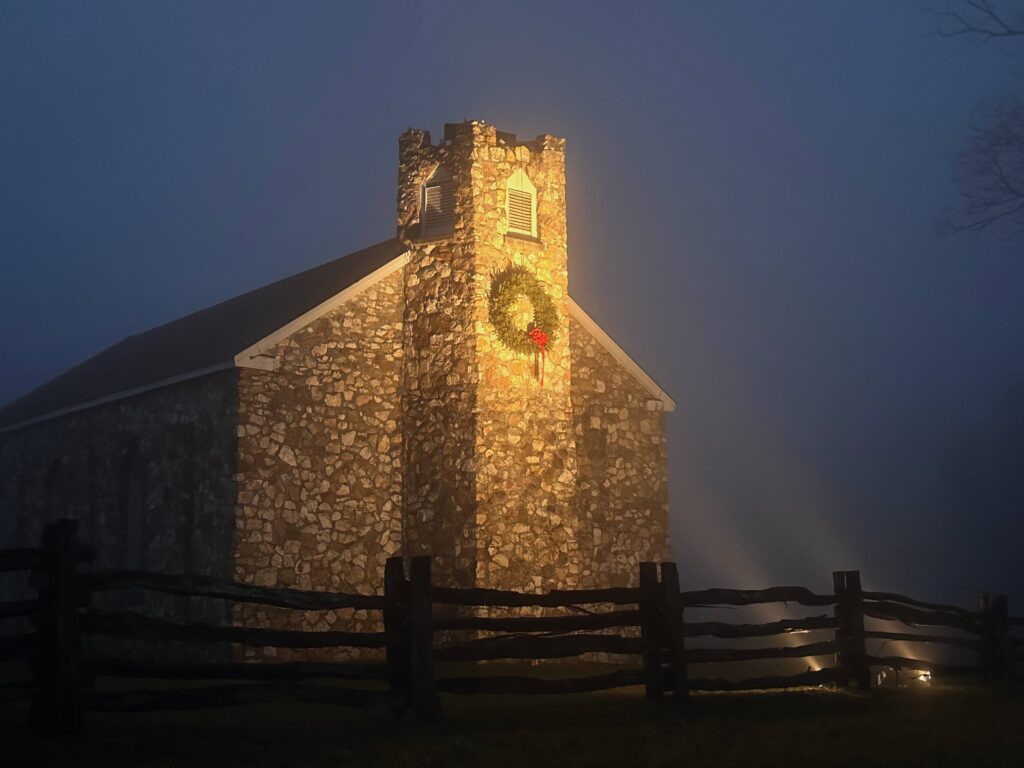
Several of these pictures was from a photo album given to me by the church when I finished my year. I know I have other pictures of Doug and some with his mother when they made the trip to Cedar City. I am sure I also have others of Rudi. They were probably taken on slides and stored in one of several large tubs in storage. The photo of the old Community Presbyterian Church of Cedar City was taken from the church’s website.
Other Virginia City Stories:
Riding the Virginia and Truckee
Christmas Eve on the Comstock, 1988
I have often used stories about my time in Virginia City in sermons. In this recent sermon, I spoke of my uneasiness during my move to Virginia City.